NASA satellites show how the wild fire crisis in California was years in the creation
Wild fires in southern California continue to burn in Los Angeles County, and newly discovered satellite images show how recent meteorological events provide fuel for the flames.
According to NASA Landsats, warm and dry weather in Los Angeles in the last two -thirds of 2024, the rough vegetation to ignite, and to spread that fire rapidly.
The largest fires started On January 7, the devastated parts of LA, including the Pacific Palisadi and Altadena. Fires spread quickly due to dry conditions and East that blasted the fires around the city and Started new flamesS
According to Mud fireThe two largest fires – Ethan’s Palisades and Fires – are 98% and 99% respectively. Taken together, the two flames burned 37,000 acres (150 square kilometers). Satellite images offer a retrospective view of how the fire seeds have been sown by the last climatological trends.
A team of researchers at the University of California, Los Angeles, found That the accumulation of vegetation between 2022 and 2024, followed by the aforementioned dry conditions, was made by Los Angeles Giant Tinderbox.
2022 and 2023 were especially humid years for southern California; According to an observatory of NASA land releaseRainfall for the center of LA were almost twice the average and two years, according to 1877 data.
The atmospheric rivers are Regular events On the west coast, especially the Pacific northwest. Atmospheric rivers are air moisture corridors that are more than 1.245 miles long (2000 kilometers) and less than 620 miles (1000 km), according to wide NASA Hydrometology Research CouncilS Rivers eject rainfall over an area for an extended period of time, often causing floods and landslidesS
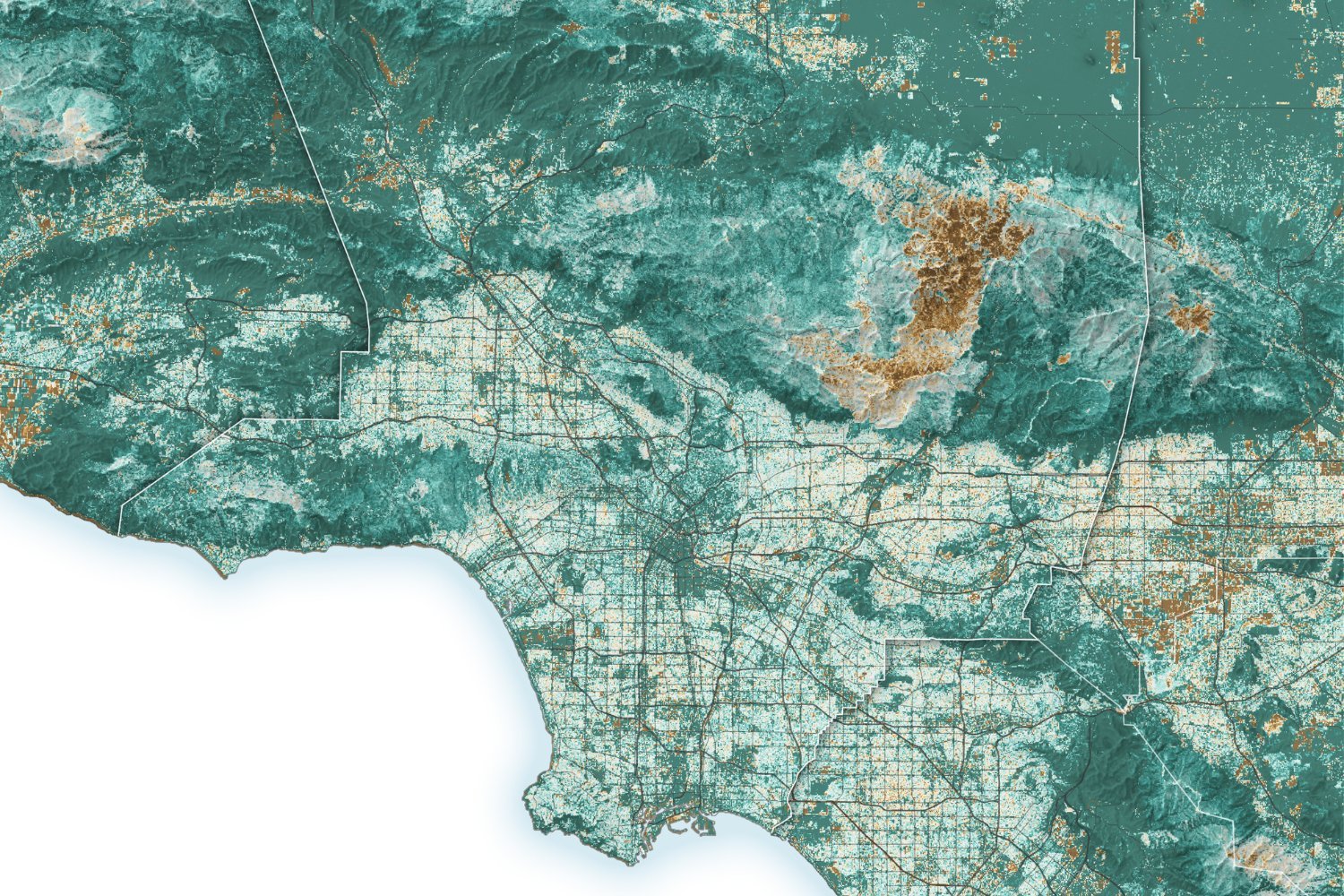
But humidity also quenches the thirst of plants, as shown on the map above. Vegetation built in La County – up to 30% more than average in some parts of the city – in the summer 2024 the national interdepartmental fire requested In July, above average vegetation was offered as a fuel for burning fires in California.
Map of soil moisture in La County. Photo: Michala Garrison, using Landsat data from US geological studies and moisture data from the soil from short -term research and transition to NASA forecasting forecasting (SPOR).
In the second half of 2024, conditions changed quickly. The area dried, in turn, uttered all the vegetation, which has spread over the years of heavy rainfall. According to Los Angeles TimesThe period from May 2024 to January 2025 is the second smallest of the record dating from 1877.
In the map above the dry soil is exposed. The map shows the moisture levels in the soil compared to the normal 40 inches of soil – where most plants lie their roots. The card reflects the moisture conditions in the soil on January 7 – the day when the two largest fires began.
Cards are a reminder that although the fires feel sudden and surprising, Earth conditions were prepared for disaster. As climate swings from very wet to very dry become more oftenIt is essential that we have satellites that explore areas and – better – to give as much warning as possible if the disaster is around the corner.