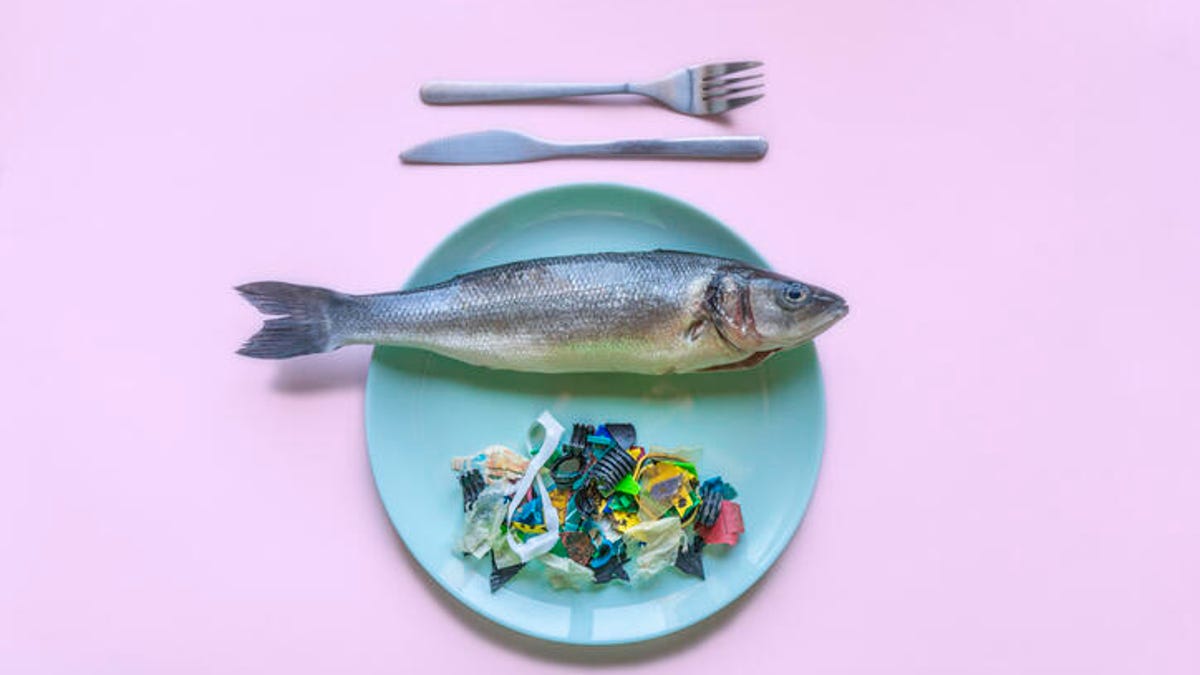Do you consume microplasty? 10 foods that secretly hide them
Microplasty has been below the microscope lately, especially considering that it is estimated that people consume between 39,000 and 52,000 microplastic particles annually. This number reaches 74,000 to 121,000 particles when you include those in which we breathe. Microplasty has become such a part of our lives that a new study found Plastic spoon value of small plastic pieces in human brain tissue. That sounds bad, but exactly how bad is it?
In order to dig deeper, we talked to a family doctor about what is considered a “safe” level of microplasty, in which foods they hide and how to limit your exposure.
How many microplastics are too many?
“There is no officially established level of” safe “or” dangerous “microplastic intake. It makes sense to want your exposure to be as low as possible”, MercleAn osteopathic physician for family medicine said in an email.
Microplastics can enter our food due to contamination where food is grown, grown or processed. Mercola explained that the use of plastic mulch and plastic seeds in agriculture and irrigation with contaminated water are among the different ways in which microplasty may be in food. Plastic packaging, utensils and containers are additional sources.
According to the US Food and Drug Administration, present Evidence does not suggest that food levels in food are a risk to us. However, you may still want to minimize how many microplastics you passively consume. These are the most common foods that contain microplasty and the measures you can take to reduce your plastic intake.
Top 10 foods in your diet that contain microplastics
Seafood
One of the most important ways to find plastic particles in our food is through disposable plastic, which fall apart and find the path in waterways and soil. When they reach the oceans, they find themselves in our seafood.
“The microplastics are then absorbed by plankton and are fooled by fish and selfish food,” Merkola said. “Small particles accumulate in the flesh … Then they find themselves on our plates.”
A recent study published by Portland State University has discovered a variety of microplastics in 180 of 182 tested seafood Samples. Microfibers are the most common type of microplastic present, but this is not the only type that turns out to be in our oceans.
Tea bags
Often used plastic called polypropylene Make tea bagsAnd even if you choose paper bags for tea, there may still be microplastics in them. The problem is that when the bags are connected to hot water, the microplasty can be placed in your tea.
Researchers at Barcelona Autonomous University have found that Polypropylene tea bags can release plastic particles in billions And nylon and cellulose tea bags can be released into millions.
How to avoid it: You don’t have to stop drinking tea. Switch to tea with free leaves and invest in a Stainless steel diffuser To enjoy your tea without microplastics.
Rice
Rice is also a hot place for microplasty. A study by the University of Queensland found that for each half cup of rice there is 3 to 4 milligrams of plasticS If you use immediate rice packages, this number is four times higher, at 13 milligrams.
How to avoid it: The study found that Washing your rice It can reduce plastic contamination by 20% to 40%, although it is worth noting that the study uses filtered water for rinsing.
Salt and sugar
When you supplement your dinner by sprinkling salt, you get an involuntary side of the microplastics. It’s hard to outstrip salt. It is in almost everything we eat, and our bodies need a certain amount of sodium to maintain our liquids and electrolytes balanced.
Unfortunately, a study found that this 90% of the 39 brands of salt marks Worldwide contains microplasty. This is probably the result of environmental pollution and the production and packaging process, which includes plastic. Microplastics were also Located in sugarS
How to avoid it: To reduce the exposure of microplastics in your salt and sugar, you can buy them packed in glass or cardboard.
Bottled water
Bottled water is one of the most famous sources of micro and nanoplasty. A study calculated that there was around 240,000 plastic particles In a liter of bottled water. Most plastic water bottles you buy in the store are made of polyethylene terephthalate or pet, plastic, so it was not surprising to see that it was presented. The plastic particles decay when the bottles are squeezed or exposed to heat. And PET plastic is not the only type of nanoplastic researchers have found in plastic bottles of water.
How to avoid it: Drinking tap water from a stainless steel or glass container It can reduce the risk of ingestion of plastic particles.
Darling
You may not expect your Darling To bring microplasty, but it is even in a glass jar. Microplastic fibers can be traced to bees and contamination. A study examining whether microplastics engulfed or carried by bees are then included in established hives that bees can continue Dispersion Through honey.
How to avoid it: Buying honey from local beekeepers, which often use more natural and durable harvest methods can reduce the risk of microplastic contamination.
Fruits and vegetables
Vegetables and fruits are an essential part of a balanced diet. Unfortunately, they can also contain microplasty. A study that took a sample fruits and vegetables find out The apples were the most The contaminated fruits and carrots were the most polluted vegetable. How is this happening?
“The plants have been shown to absorb micro- and nanoplastics from the soil through their root systems, thus polluting edible portions,” Merkola said.
Many grocery stores also pack fruits and vegetables in plastic to keep them fresh. According to the FDA there is no sufficient evidence To determine that plastic microplastics are migrated in food. But Mercola offers you to avoid it as much as you can.
How to avoid it: Wash your fruits well, peel when possible, and choose for local or organic production.
Protein
A recent survey of Ocean Conservancy researchers found that this 88% of vegetable and animal proteins They contain some level of microplasty. But the highly treated proteins, such as plant-based alternatives, fish sticks or chicken nuns, have stabbed the most microplastics, suggesting that microplastic pollution partly comes from dietary processingS The study found that breaded shrimp had an average of 300 microplastic pieces per serving. Vegetable nails had 100 pieces per serving.
Food processing is not the only way for microplasty to enter these sources of protein. Microplastics are in Animals And in the environment where animals are raised. Plant alternatives can be contaminated by soil or irrigation.
How to avoid it: After reading this, you may be wondering what protein you should eat. The reality is that more research is needed to know the exact levels and their impact on our health. Our bodies need protein to function, so getting enough is important, no matter which source you choose.
Read more: Easily visual protein guide to help you reach maximum muscle profits
What do microplastics mean in food?
So, do all microplasty foods contain? I can’t say for sure. However, I can tell you that more research is needed to understand how eating microplasty foods affects us. However, although long -term health effects remain in the process of examination, microplasty is something to be careful about and protect yourself if you can, as Mercula explains.
“The absorbed microplasty has been found to accumulate in the circulatory system and various organs, including the brain, where they can cause inflammation and tissue damage,” says Merk.
Other potential side effects are the hormonal imbalances caused by Endocrine -destructive chemicals It is located in plastics. Microplastics can also absorb others Ecological toxins and enter them into the body.
There is no safe level of microplasty and we cannot completely outstrip them: they are everywhere and in everything. But it is a good idea to minimize the exposure where you can.
Expert tips to reduce microplasty intake
You can reduce by following this advice:
Be careful how many mussels you eat
Mussels like mussels, oysters and combs have higher levels of microplasty, so don’t overdo it.
Avoid storage containers made of plastic
This is one of Mercola’s biggest suggestions because of the “plastic chemicals” in plastic. BPA and phthalates are endocrine destructive chemicals that can transfer from plastic to food. They are fat, so this happens most easily with fatty foods. It is best to store fat foods in glass containers. You can store dry foods in plastic, if necessary.
Avoid foods with plastic packaging
It can be easier to say than to do, but it is something to strive for in areas where you can make the switch.
Get rid of plastic kitchen utensils
From the spoons we use to stir our sauces to the cutting boards we use to cut our vegetables, if they are plastic, you absorb microplasty. A good rule is: everything plastic, which comes in contact with your food, must be replaced for ceramics, glass, stainless steel or wood.
To deal with the overall number of microplastics in the food, you can install a filter in your clothing machine. If you can afford it, a special filter will catch microfibri before contaminating water systems. Thehe PlanetCare 2.0 Microfiber Filter Starts at $ 125.
We still have a lot to learn about microplastics and their long -term effects on our health when they are swallowed. It may be difficult to hear that they are so many of our foods, but it should not deter you to eat well. A Balanced diet of protein, fruits and vegetables will ensure that your body has enough fuel to Function and flourishing – Microplasty or not.